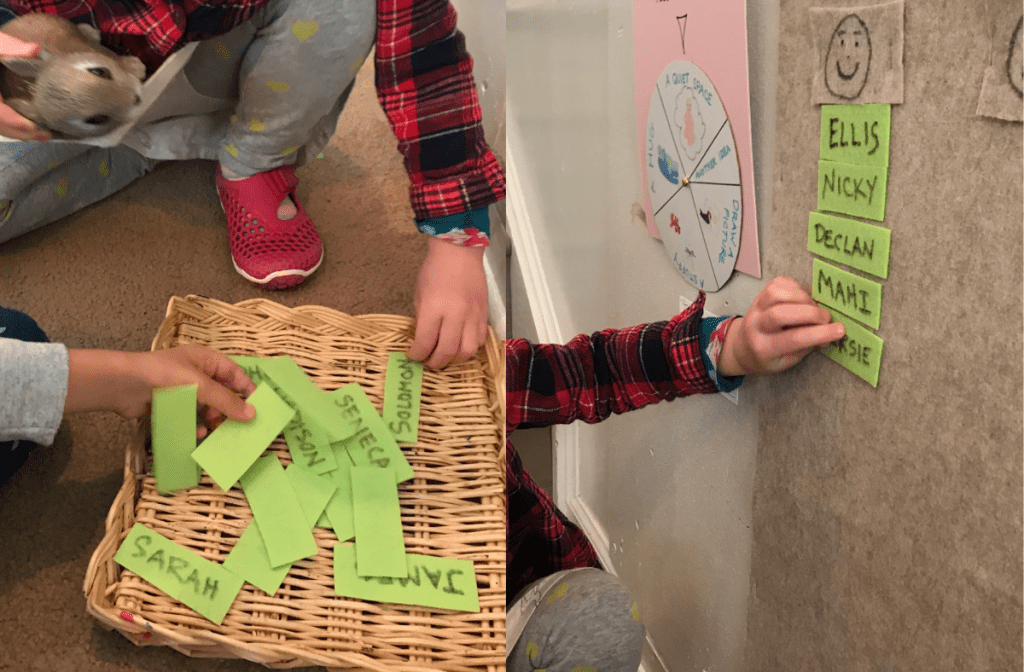A Guide for Caregivers Helping Their Children Become Part of a More Just & Decent World
Raising children is hard. It can be beautiful, fun, and rewarding — but it is challenging, too. Caregivers and parents are often desperate for support, ideas, and concrete ways of answering our children’s big questions.
As a child psychologist, I hear many of those questions from kids and from parents. Their big concerns are about how people get along, why the world works the way it does, what is fair, and how to understand themselves. Many of their big and, frankly, toughest questions involve race.
With such a contentious topic and the many dynamic feelings and opinions, our job as caregivers can seem impossible.
Parents ask and tell me:
- “What do I tell my young child about race anyway?”
- “I don’t want them to learn about race in the ways that I did.”
- “How can I protect them from discussions they aren’t ready for?”
These are all questions I’ve heard from caregivers over my years of practice. I hear families, educators, and others serving children saying that they need help. They need the help of folks who understand children and who have had these conversations before. They also want access to the research about what this all means for kids and families.
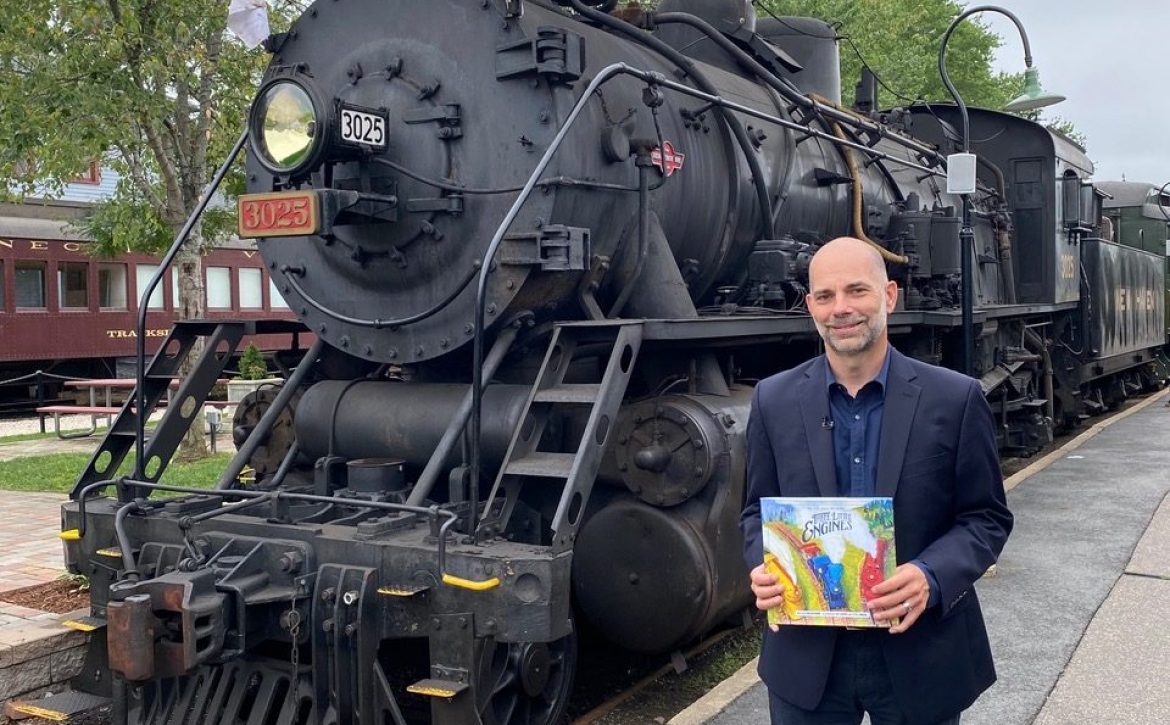
The new guide, “Discussing Race with Young Children: A Step-by-Step Activity Guide,” is a most welcome resource for every young family! It doesn’t solve all the problems related to race, but is a helpful guide for caregivers who want to support our children in becoming part of a more just and decent world. This guide was created with children’s stories, questions, and experiences at the heart of it. It was also created with a clear understanding of what caregivers are facing — the questions, stories, and conflicts that commonly arise.
The work here is well-researched and supported by many experts who understand children’s needs. Most importantly, this guide provides an opportunity to really listen to our children and to be in conversation with them — and it encourages us, as caregivers, to grow and learn with them.
This guide accompanies us as we play, listen, and learn with our children. I am sure that in these conversations and guides, you will come up with even more questions — but you will also learn something new and feel supported. This is not easy work, but with help like this guide provides, it can be beautiful, fun, and rewarding.